【Drupal】新しいエンティティタイプを使用して独自テーブルと編集用UIを作成する

Drupalのサンプルコードから新しいエンティティタイプを作成するサンプルコードを利用して、新規マスターテーブルとマスターテーブルを編集するためのUIを作成しました。
開発者はテーブル定義を規定されたルールで配列変数に格納するだけで、DrupalCoreが必要に応じてマスターテーブルを作成します。テーブルに対する読み書きは通常のNODEエンティティと同様の方法で可能なので、可読性の高いコードを書くことができます。この手法でデータベースのアクセスを行えば、決まった手順で実施できるため不具合が入り込む余地が激減します。
Drupal でコンテンツ エンティティ タイプを作成する
このページでは、Drupal 8 の管理管理ページを含むコンテンツ エンティティ タイプを作成する方法の例を示します。
人 (連絡先) を追加、編集、削除するための「連絡先」エンティティを作成する方法を説明します。 Entity は完全にフィールド化可能で、Drupal 8 で利用可能な新しいエンティティ概念のほとんどを使用します。
ノート:
- このガイドでは、コンテンツ エンティティ タイプを作成するコードの記述方法を説明します。 ただし、代わりに Drush を使用すると、このガイドをバイパスできます。 Drush を使用すると、コマンド ラインから次のコマンドを使用して新しいコンテンツ エンティティ タイプを作成できます。
drush generate entity:content. - このガイドのこのコードは、
ContentEntityExampleDrupal Examples モジュールのこのモジュールは、 https://www.drupal.org/project/examples からダウンロードできます。
評価用モジュールの作成
まずは評価用のモジュールを作成します。
ここではファイル名をcontent_entity_exampleとしています。
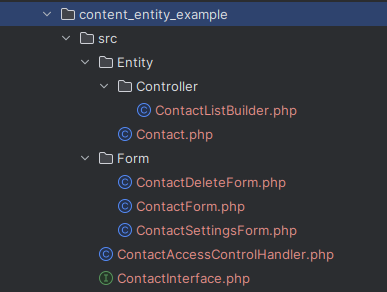
フォルダ名と同じ名前でinfo.ymlファイルを作成して、インストールするための情報を設定します。
content_entity_example.info.yml
name: Content Entity Example
type: module
description: 'Provides ContentEntityExampleContact entity.'
package: Example modules
core: 8.x
# These modules are required by the tests, must be available at bootstrap time
dependencies:
- options
- entity_reference
- examples
権限
カスタム権限を設定します。
content_entity_example.permissions.yml
view contact entity:
title: 'View Contact entity'
add contact entity:
title: 'Add Contact entity'
edit contact entity:
title: 'Edit Contact Entity'
delete contact entity:
title: 'Delete Contact entity'
administer contact entity:
title: 'Administer Contact entity'
restrict access: TRUE
カスタム権限を設定すると管理者画面のユーザ->権限の権限一覧に表示されます。
権限設定のUI(管理画面)
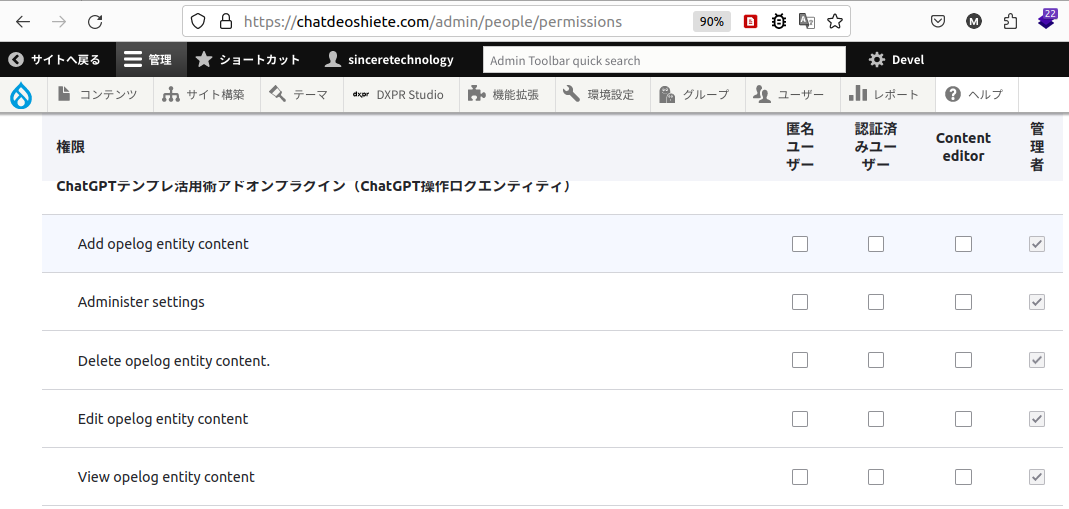
詳細はこちらを参照ください
Permissions should be defined in a permissions.yml file or a permission callback
ルーティング
エンティティの参照、追加、編集、削除などのアクション用のURLパラメータをここで定義します。
ただし、ENTITYクラスを使用しているため、CALL BACK用のコントローラやフォームクラスは、ENTITYクラス内で定義されています。
content_entity_example.routing.yml
# This file brings everything together. Very nifty!
# Route name can be used in several places; e.g. links, redirects, and local
# actions.
entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical:
path: '/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}'
defaults:
# Calls the view controller, defined in the annotation of the contact entity
_entity_view: 'content_entity_example_contact'
_title: 'Contact Content'
requirements:
# Calls the access controller of the entity, $operation 'view'
_entity_access: 'content_entity_example_contact.view'
entity.content_entity_example_contact.collection:
path: '/content_entity_example_contact/list'
defaults:
# Calls the list controller, defined in the annotation of the contact entity.
_entity_list: 'content_entity_example_contact'
_title: 'Contact List'
requirements:
# Checks for permission directly.
_permission: 'administer contact entity'
content_entity_example.contact_add:
path: '/content_entity_example_contact/add'
defaults:
# Calls the form.add controller, defined in the contact entity.
_entity_form: content_entity_example_contact.add
_title: 'Add Contact'
requirements:
_entity_create_access: 'content_entity_example_contact'
entity.content_entity_example_contact.edit_form:
path: '/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/edit'
defaults:
# Calls the form.edit controller, defined in the contact entity.
_entity_form: content_entity_example_contact.edit
_title: 'Edit Contact'
requirements:
_entity_access: 'content_entity_example_contact.edit'
entity.content_entity_example_contact.delete_form:
path: '/contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/delete'
defaults:
# Calls the form.delete controller, defined in the contact entity.
_entity_form: content_entity_example_contact.delete
_title: 'Delete Contact'
requirements:
_entity_access: 'content_entity_example_contact.delete'
content_entity_example.contact_settings:
path: 'admin/structure/content_entity_example_contact_settings'
defaults:
_form: '\Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactSettingsForm'
_title: 'Contact Settings'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer contact entity'
エンティティ注釈の「リンク」セクションで定義されたアクションのルート名は、正しいパターンに従う必要があります。 詳細については、以下のコンテンツ エンティティ クラスを参照してください。
対象フォームのクラス設定(_entity_formの設定)
例えば、編集用フォームを定義する場合は、_entity_form に対象のENTITYクラスとENTITYクラス内で定義されている編集用フォームクラスに紐づくIDを設定します。
_entity_form: {ENTITYクラス名}.{ENTITYクラス内で定義されている編集用フォームクラスに紐づくID}
entity.content_entity_example_contact.edit_form:
path: '/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/edit'
defaults:
# Calls the form.edit controller, defined in the contact entity.
_entity_form: content_entity_example_contact.edit
_title: 'Edit Contact'
requirements:
_entity_access: 'content_entity_example_contact.edit'
メニュー
content_entity_example.links.menu.yml
ルーティング ファイルと組み合わせて、これはモジュールのhook_menuを置き換えます。
# Define the menu links for this module
entity.content_entity_example_contact.collection:
title: 'Content Entity Example: Contacts Listing'
route_name: entity.content_entity_example_contact.collection
description: 'List Contacts'
parent: system.admin_structure
weight: 10
content_entity_example_contact.admin.structure.settings:
title: Contact Settings
description: 'Configure Contact entity'
route_name: content_entity_example.contact_settings
parent: system.admin_structure
アクション
content_entity_example.links.action.yml
# All action links for this module
content_entity_example.contact_add:
# Which route will be called by the link
route_name: content_entity_example.contact_add
title: 'Add Contact'
# Where will the link appear, defined by route name.
appears_on:
- entity.content_entity_example_contact.collection
- entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical
リンク
content_entity_example.links.task.yml
エンティティ表示ページに「表示/編集/削除」タブが表示されます。
エンティティ設定ページに「設定」タブが表示されます。
# Define the 'local' links for the module
contact.settings_tab:
route_name: content_entity_example.contact_settings
title: Settings
base_route: content_entity_example.contact_settings
contact.view:
route_name: entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical
base_route: entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical
title: View
contact.page_edit:
route_name: entity.content_entity_example_contact.edit_form
base_route: entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical
title: Edit
contact.delete_confirm:
route_name: entity.content_entity_example_contact.delete_form
base_route: entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical
title: Delete
weight: 10
エンティティタイプクラス
src/ContactInterface.php
エンティティへのパブリック アクセスを定義するインターフェイスを提供することをお勧めします。 さらに、「EntityOwnerInterface」を呼び出して追加機能にアクセスします。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityInterface;
use Drupal\user\EntityOwnerInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityChangedInterface;
/**
* Provides an interface defining a Contact entity.
* @ingroup content_entity_example
*/
interface ContactInterface extends ContentEntityInterface, EntityOwnerInterface, EntityChangedInterface {
}
?>
src/Entity/Contact.php
このファイルは Contact エンティティ クラスを定義します。
データベース スキーマはベース フィールドの定義から自動的に決定され、モジュールのインストール中に対応するテーブルがデータベース内にセットアップされます。
ルーティング セクションで述べたように、「リンク」セクションのルートは正しいパターンに従う必要があります。 これについては、以下の注釈セクションに記載されています。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example\Entity;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityStorageInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Field\BaseFieldDefinition;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityBase;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityTypeInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityChangedTrait;
use Drupal\content_entity_example\ContactInterface;
use Drupal\user\UserInterface;
/**
* Defines the Contact entity.
*
* @ingroup content_entity_example
*
* This is the main definition of the entity type. From it, an entityType is
* derived. The most important properties in this example are listed below.
*
* id: The unique identifier of this entityType. It follows the pattern
* 'moduleName_xyz' to avoid naming conflicts.
*
* label: Human readable name of the entity type.
*
* handlers: Handler classes are used for different tasks. You can use
* standard handlers provided by D8 or build your own, most probably derived
* from the standard class. In detail:
*
* - view_builder: we use the standard controller to view an instance. It is
* called when a route lists an '_entity_view' default for the entityType
* (see routing.yml for details. The view can be manipulated by using the
* standard drupal tools in the settings.
*
* - list_builder: We derive our own list builder class from the
* entityListBuilder to control the presentation.
* If there is a view available for this entity from the views module, it
* overrides the list builder. @todo: any view? naming convention?
*
* - form: We derive our own forms to add functionality like additional fields,
* redirects etc. These forms are called when the routing list an
* '_entity_form' default for the entityType. Depending on the suffix
* (.add/.edit/.delete) in the route, the correct form is called.
*
* - access: Our own accessController where we determine access rights based on
* permissions.
*
* More properties:
*
* - base_table: Define the name of the table used to store the data. Make sure
* it is unique. The schema is automatically determined from the
* BaseFieldDefinitions below. The table is automatically created during
* installation.
*
* - fieldable: Can additional fields be added to the entity via the GUI?
* Analog to content types.
*
* - entity_keys: How to access the fields. Analog to 'nid' or 'uid'.
*
* - links: Provide links to do standard tasks. The 'edit-form' and
* 'delete-form' links are added to the list built by the
* entityListController. They will show up as action buttons in an additional
* column.
*
* There are many more properties to be used in an entity type definition. For
* a complete overview, please refer to the '\Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityType'
* class definition.
*
* The following construct is the actual definition of the entity type which
* is read and cached. Don't forget to clear cache after changes.
*
* @ContentEntityType(
* id = "content_entity_example_contact",
* label = @Translation("Contact entity"),
* handlers = {
* "view_builder" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityViewBuilder",
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\ContactListBuilder",
* "views_data" = "Drupal\views\EntityViewsData",
* "form" = {
* "add" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactDeleteForm",
* },
* "access" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\ContactAccessControlHandler",
* },
* base_table = "contact",
* admin_permission = "administer contact entity",
* fieldable = TRUE,
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "id",
* "label" = "name",
* "uuid" = "uuid"
* },
* links = {
* "canonical" = "/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}",
* "edit-form" = "/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/edit",
* "delete-form" = "/contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/delete",
* "collection" = "/content_entity_example_contact/list"
* },
* field_ui_base_route = "content_entity_example.contact_settings",
* )
*
* The 'links' above are defined by their path. For core to find the corresponding
* route, the route name must follow the correct pattern:
*
* entity.<entity-name>.<link-name> (replace dashes with underscores)
* Example: 'entity.content_entity_example_contact.canonical'
*
* See routing file above for the corresponding implementation
*
* The 'Contact' class defines methods and fields for the contact entity.
*
* Being derived from the ContentEntityBase class, we can override the methods
* we want. In our case we want to provide access to the standard fields about
* creation and changed time stamps.
*
* Our interface (see ContactInterface) also exposes the EntityOwnerInterface.
* This allows us to provide methods for setting and providing ownership
* information.
*
* The most important part is the definitions of the field properties for this
* entity type. These are of the same type as fields added through the GUI, but
* they can by changed in code. In the definition we can define if the user with
* the rights privileges can influence the presentation (view, edit) of each
* field.
*/
class Contact extends ContentEntityBase implements ContactInterface {
use EntityChangedTrait; // Implements methods defined by EntityChangedInterface.
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* When a new entity instance is added, set the user_id entity reference to
* the current user as the creator of the instance.
*/
public static function preCreate(EntityStorageInterface $storage_controller, array &$values) {
parent::preCreate($storage_controller, $values);
$values += array(
'user_id' => \Drupal::currentUser()->id(),
);
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getCreatedTime() {
return $this->get('created')->value;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getOwner() {
return $this->get('user_id')->entity;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getOwnerId() {
return $this->get('user_id')->target_id;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function setOwnerId($uid) {
$this->set('user_id', $uid);
return $this;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function setOwner(UserInterface $account) {
$this->set('user_id', $account->id());
return $this;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* Define the field properties here.
*
* Field name, type and size determine the table structure.
*
* In addition, we can define how the field and its content can be manipulated
* in the GUI. The behaviour of the widgets used can be determined here.
*/
public static function baseFieldDefinitions(EntityTypeInterface $entity_type) {
// Standard field, used as unique if primary index.
$fields['id'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('integer')
->setLabel(t('ID'))
->setDescription(t('The ID of the Contact entity.'))
->setReadOnly(TRUE);
// Standard field, unique outside of the scope of the current project.
$fields['uuid'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('uuid')
->setLabel(t('UUID'))
->setDescription(t('The UUID of the Contact entity.'))
->setReadOnly(TRUE);
// Name field for the contact.
// We set display options for the view as well as the form.
// Users with correct privileges can change the view and edit configuration.
$fields['name'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('string')
->setLabel(t('Name'))
->setDescription(t('The name of the Contact entity.'))
->setSettings(array(
'default_value' => '',
'max_length' => 255,
'text_processing' => 0,
))
->setDisplayOptions('view', array(
'label' => 'above',
'type' => 'string',
'weight' => -6,
))
->setDisplayOptions('form', array(
'type' => 'string_textfield',
'weight' => -6,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('form', TRUE)
->setDisplayConfigurable('view', TRUE);
$fields['first_name'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('string')
->setLabel(t('First Name'))
->setDescription(t('The first name of the Contact entity.'))
->setSettings(array(
'default_value' => '',
'max_length' => 255,
'text_processing' => 0,
))
->setDisplayOptions('view', array(
'label' => 'above',
'type' => 'string',
'weight' => -5,
))
->setDisplayOptions('form', array(
'type' => 'string_textfield',
'weight' => -5,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('form', TRUE)
->setDisplayConfigurable('view', TRUE);
// Gender field for the contact.
// ListTextType with a drop down menu widget.
// The values shown in the menu are 'male' and 'female'.
// In the view the field content is shown as string.
// In the form the choices are presented as options list.
$fields['gender'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('list_string')
->setLabel(t('Gender'))
->setDescription(t('The gender of the Contact entity.'))
->setSettings(array(
'allowed_values' => array(
'female' => 'female',
'male' => 'male',
),
))
->setDisplayOptions('view', array(
'label' => 'above',
'type' => 'list_default',
'weight' => -4,
))
->setDisplayOptions('form', array(
'type' => 'options_select',
'weight' => -4,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('form', TRUE)
->setDisplayConfigurable('view', TRUE);
// Owner field of the contact.
// Entity reference field, holds the reference to the user object.
// The view shows the user name field of the user.
// The form presents a auto complete field for the user name.
$fields['user_id'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('entity_reference')
->setLabel(t('User Name'))
->setDescription(t('The Name of the associated user.'))
->setSetting('target_type', 'user')
->setSetting('handler', 'default')
->setDisplayOptions('view', array(
'label' => 'above',
'type' => 'entity_reference_label',
'weight' => -3,
))
->setDisplayOptions('form', array(
'type' => 'entity_reference_autocomplete',
'settings' => array(
'match_operator' => 'CONTAINS',
'size' => 60,
'autocomplete_type' => 'tags',
'placeholder' => '',
),
'weight' => -3,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('form', TRUE)
->setDisplayConfigurable('view', TRUE);
$fields['langcode'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('language')
->setLabel(t('Language code'))
->setDescription(t('The language code of Contact entity.'));
$fields['created'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('created')
->setLabel(t('Created'))
->setDescription(t('The time that the entity was created.'));
$fields['changed'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('changed')
->setLabel(t('Changed'))
->setDescription(t('The time that the entity was last edited.'));
return $fields;
}
}
?>
アノテーションの設定
アノテーションとはあらかじめアノテーションクラスで定義されたフォーマットでコメント領域に設定された意味のある情報のことをいいます。
* @ContentEntityType(
* id = "content_entity_example_contact",
* label = @Translation("Contact entity"),
* handlers = {
* "view_builder" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityViewBuilder",
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\ContactListBuilder",
* "views_data" = "Drupal\views\EntityViewsData",
* "form" = {
* "add" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\Form\ContactDeleteForm",
* },
* "access" = "Drupal\content_entity_example\ContactAccessControlHandler",
* },
* base_table = "contact",
* admin_permission = "administer contact entity",
* fieldable = TRUE,
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "id",
* "label" = "name",
* "uuid" = "uuid"
* },
* links = {
* "canonical" = "/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}",
* "edit-form" = "/content_entity_example_contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/edit",
* "delete-form" = "/contact/{content_entity_example_contact}/delete",
* "collection" = "/content_entity_example_contact/list"
* },
* field_ui_base_route = "content_entity_example.contact_settings",
* )
この例では、以下の項目が設定されています。
| 項目 | 設定内容 | 備考 |
|---|---|---|
id | 対象ENTITYクラスのID | |
label | 対象ENTITYクラスのラベル名 | |
handlers | 各種ハンドラークラスの定義 | |
| forms | 各種フォームクラスの定義 | |
| access | アクセスハンドラー用クラス定義 | |
base_table | ベーステーブル名 | |
admin_permission | 権利者用権限 | |
fieldable | ||
entity_keys | キーの定義 | |
links | ハンドラーにデータを渡すためのパラメータ | |
| field_ui_base_route | routing.ymlで定義済みの管理者用設定情報 |
フォーム
src/フォーム/ContactForm.php
連絡先エンティティのコンテンツを追加および編集するためのフォームを定義します。
これは、ルーティングの「_entity_form」定義によって呼び出されます。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityForm;
use Drupal\Core\Language\Language;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
/**
* Form controller for the content_entity_example entity edit forms.
*
* @ingroup content_entity_example
*/
class ContactForm extends ContentEntityForm {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
/* @var $entity \Drupal\content_entity_example\Entity\Contact */
$form = parent::buildForm($form, $form_state);
$entity = $this->entity;
$form['langcode'] = array(
'#title' => $this->t('Language'),
'#type' => 'language_select',
'#default_value' => $entity->getUntranslated()->language()->getId(),
'#languages' => Language::STATE_ALL,
);
return $form;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function save(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$status = parent::save($form, $form_state);
$entity = $this->entity;
if ($status == SAVED_UPDATED) {
$this->messenger()
->addMessage($this->t('The contact %feed has been updated.', ['%feed' => $entity->toLink()->toString()]));
} else {
$this->messenger()
->addMessage($this->t('The contact %feed has been added.', ['%feed' => $entity->toLink()->toString()]));
}
$form_state->setRedirectUrl($this->entity->toUrl('collection'));
return $status;
}
}
?>
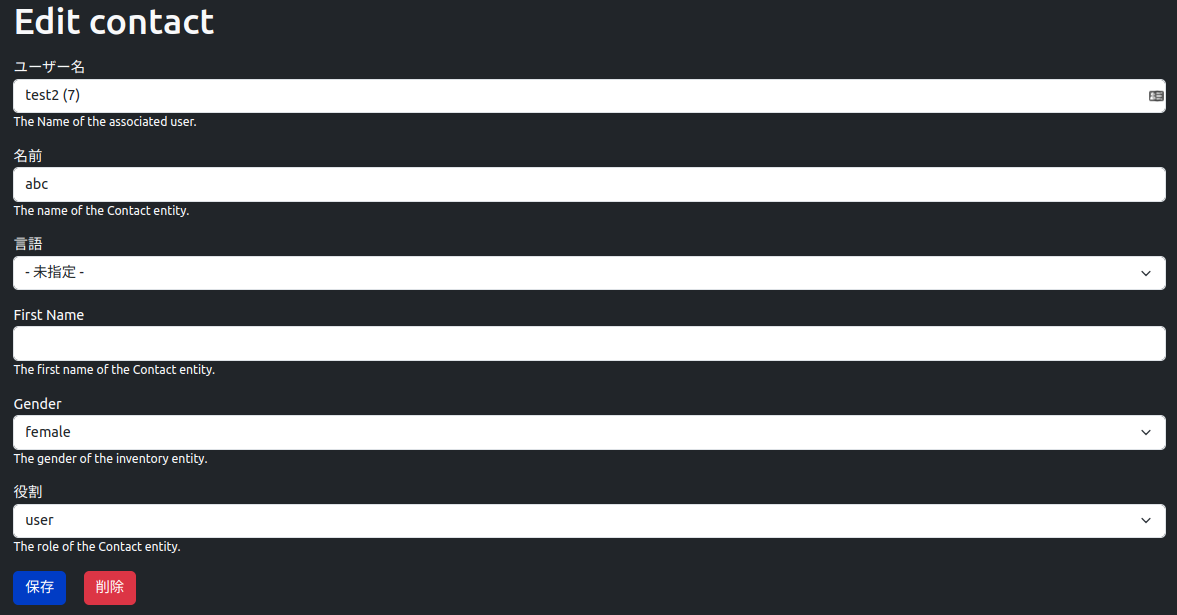
編集フォームのUI
編集フォームはDrupalCoreのデフォルトのUIを使用して表示します。
src/フォーム/ContactDeleteForm.php
連絡先エンティティのコンテンツを削除するときの確認フォームです。
ContentEntityConfirmFormBaseを継承します。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityConfirmFormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
/**
* Provides a form for deleting a content_entity_example entity.
*
* @ingroup content_entity_example
*/
class ContactDeleteForm extends ContentEntityConfirmFormBase {
/**
* Returns the question to ask the user.
*
* @return string
* The form question. The page title will be set to this value.
*/
public function getQuestion() {
return $this->t('Are you sure you want to delete %name?', array('%name' => $this->entity->label()));
}
/**
* Returns the route to go to if the user cancels the action.
*
* @return \Drupal\Core\Url
* A URL object.
*/
public function getCancelUrl() {
return new Url('entity.content_entity_example_contact.collection');
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getConfirmText() {
return $this->t('Delete');
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* Delete the entity and log the event. logger() replaces the watchdog.
*/
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$entity = $this->getEntity();
$entity->delete();
$this->logger('content_entity_example')->notice('deleted %title.',
array(
'%title' => $this->entity->label(),
));
// Redirect to term list after delete.
$form_state->setRedirect('entity.content_entity_example_contact.collection');
}
}
?>
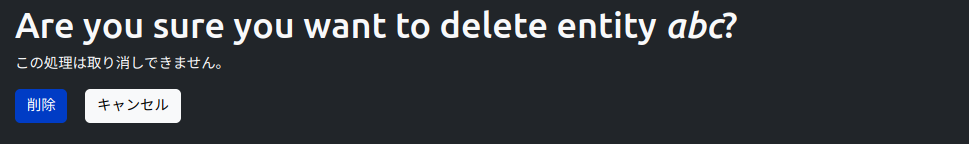
削除フォームのUI
編集フォームはDrupalCoreのデフォルトのUIを使用して表示します。
src/フォーム/ContactSettingsForm.php
連絡先の設定フォームを作成します。 ここからフィールドを管理できます。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
/**
* Class ContentEntityExampleSettingsForm.
* @package Drupal\content_entity_example\Form
* @ingroup content_entity_example
*/
class ContactSettingsForm extends FormBase {
/**
* Returns a unique string identifying the form.
*
* @return string
* The unique string identifying the form.
*/
public function getFormId() {
return 'content_entity_example_settings';
}
/**
* Form submission handler.
*
* @param array $form
* An associative array containing the structure of the form.
* @param FormStateInterface $form_state
* An associative array containing the current state of the form.
*/
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
// Empty implementation of the abstract submit class.
}
/**
* Define the form used for ContentEntityExample settings.
* @return array
* Form definition array.
*
* @param array $form
* An associative array containing the structure of the form.
* @param FormStateInterface $form_state
* An associative array containing the current state of the form.
*/
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$form['contact_settings']['#markup'] = 'Settings form for ContentEntityExample. Manage field settings here.';
return $form;
}
}
?>
コントローラ
src/ContactListBuilder.php
連絡先リストのヘッダーと行の内容を定義します。 「Operations」リンクは、親関数が呼び出されるときに、entityType アノテーションの「links」定義から自動的に追加されます。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityListBuilder;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
/**
* Provides a list controller for content_entity_example_contact entity.
*
* @ingroup content_entity_example
*/
class ContactListBuilder extends EntityListBuilder {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* We override ::render() so that we can add our own content above the table.
* parent::render() is where EntityListBuilder creates the table using our
* buildHeader() and buildRow() implementations.
*/
public function render() {
$build['description'] = [
'#markup' => $this->t('Content Entity Example implements a Contacts model. These contacts are fieldable entities. You can manage the fields on the <a href="@adminlink">Contacts admin page</a>.', array(
'@adminlink' => Url::fromRoute('content_entity_example.contact_settings', [], ['absolute' => 'true'])->toString(),
)),
];
$build += parent::render();
return $build;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* Building the header and content lines for the contact list.
*
* Calling the parent::buildHeader() adds a column for the possible actions
* and inserts the 'edit' and 'delete' links as defined for the entity type.
*/
public function buildHeader() {
$header['id'] = $this->t('ContactID');
$header['name'] = $this->t('Name');
$header['first_name'] = $this->t('First Name');
$header['gender'] = $this->t('Gender');
return $header + parent::buildHeader();
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildRow(EntityInterface $entity) {
/* @var $entity \Drupal\content_entity_example\Entity\Contact */
$row['id'] = $entity->id();
$row['name'] = $entity->link();
$row['first_name'] = $entity->first_name->value;
$row['gender'] = $entity->gender->value;
return $row + parent::buildRow($entity);
}
}
?>
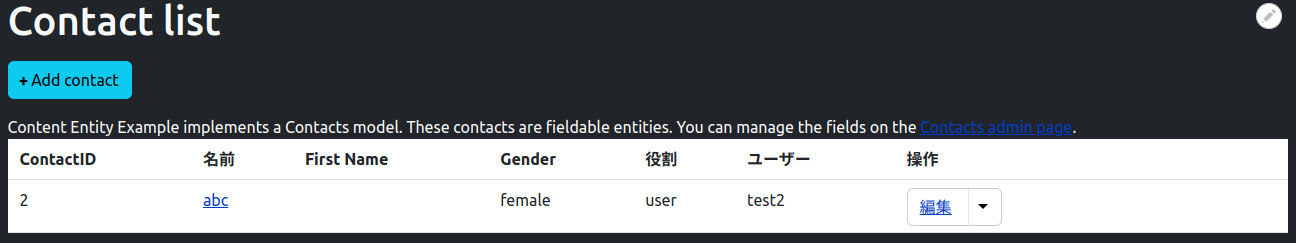
アクセス制御ハンドラ
src/ContactAccessControlHandler.php
アクセス制御ハンドラークラスを作成します。権限により各アクションの動作をここで判断します。
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_entity_example;
use Drupal\Core\Access\AccessResult;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityAccessControlHandler;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Session\AccountInterface;
/**
* Access controller for the contact entity.
*
* @see \Drupal\content_entity_example\Entity\Contact.
*/
class ContactAccessControlHandler extends EntityAccessControlHandler {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* Link the activities to the permissions. checkAccess is called with the
* $operation as defined in the routing.yml file.
*/
protected function checkAccess(EntityInterface $entity, $operation, AccountInterface $account) {
switch ($operation) {
case 'view':
return AccessResult::allowedIfHasPermission($account, 'view contact entity');
case 'edit':
return AccessResult::allowedIfHasPermission($account, 'edit contact entity');
case 'delete':
return AccessResult::allowedIfHasPermission($account, 'delete contact entity');
}
return AccessResult::allowed();
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*
* Separate from the checkAccess because the entity does not yet exist, it
* will be created during the 'add' process.
*/
protected function checkCreateAccess(AccountInterface $account, array $context, $entity_bundle = NULL) {
return AccessResult::allowedIfHasPermission($account, 'add contact entity');
}
}
?>
新しいエンティティを登録する
Contact クラスを作成する前にこのガイドの途中でモジュールを有効にした場合、Drupal はエンティティのデータベース テーブルを作成しません。 これにより、エラー ページが表示されます。
新しいエンティティを登録するには (エンティティ クラスの詳細に従ってデータベース テーブルを作成します)、次のコマンドを実行するだけです。 drush updatedb --entity-updatesまたは drupal update:entities。 このコマンドを実行すると、Drupal は新しいエンティティが見つかったことと、保留中の更新があることを通知します。 保留中の更新を適用すると、Drupal Web サイトで新しいエンティティの使用を開始できるようになります。
#2976035: エンティティ タイプの CRUD 操作では 、最後にインストールされたエンティティ タイプとフィールド ストレージ定義を 実行する機能を使用する必要があります drush entup取り除かれた。
モジュールを参照してください 「エンティティ更新の開発」 。
JSON:API との統合
デフォルトでは、モジュール jsonapi を有効にすると、対応する jsonapi URL を通じてすべてのコンテンツ エンティティ タイプが公開されます。 カスタム エンティティ タイプがこれに対応する準備ができていない場合、または単に無効にしてアクセスできないようにしたい場合は、@ContentEntityType アノテーションのルート レベルに内部属性を追加できます。
internal = TRUE,
参考
Create custom Entity Type in Drupal8 for better content management
Defining and using Content Entity Field definitions
Creating a content entity type in Drupal 8
Permissions should be defined in a permissions.yml file or a permission callback
この記事に関するご質問やご意見などございましたらお問い合わせフォームからお気軽にご連絡ください。
